Gas storage in Nanoporous materials
Porous materials including porous carbon, metal organic frameworks (MOFs), zeolites, porous organic polymer networks, porous covalent organic frameworks (COFs) etc., offer a wide variety of chemical composition and structural architectures that are suitable for the adsorption and storage of different gas molecules including hydrogen, methane and carbon dioxide. Designing nanoporous materials with high surface area, large porosity, superior structural stability and amenability to various processing conditions, is important to meet the commercial demands of large scale reversible gas storage systems. Over the last several years, we have been working on designing efficient nanoporous carbon materials for their applications in gas storage. We study the gas sorption behavior of these systems for CO2, H2 and CH4.
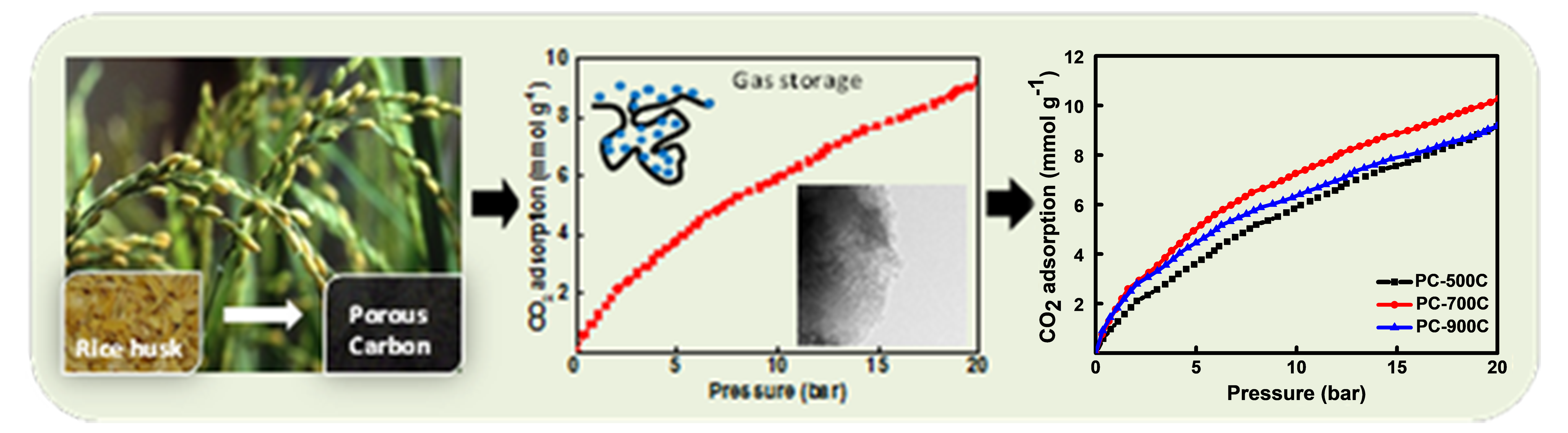
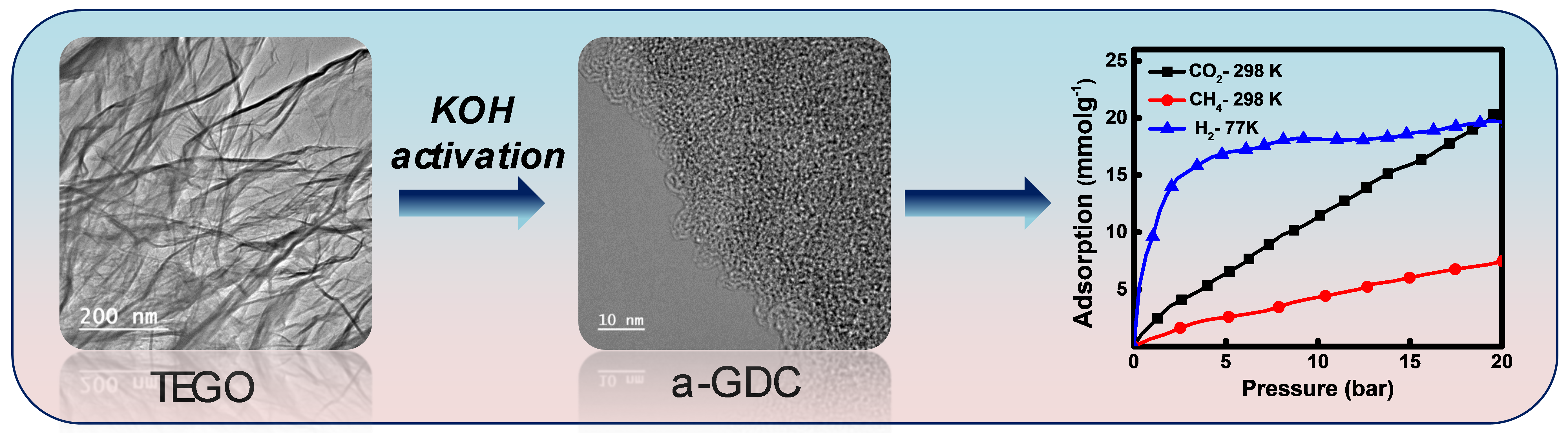
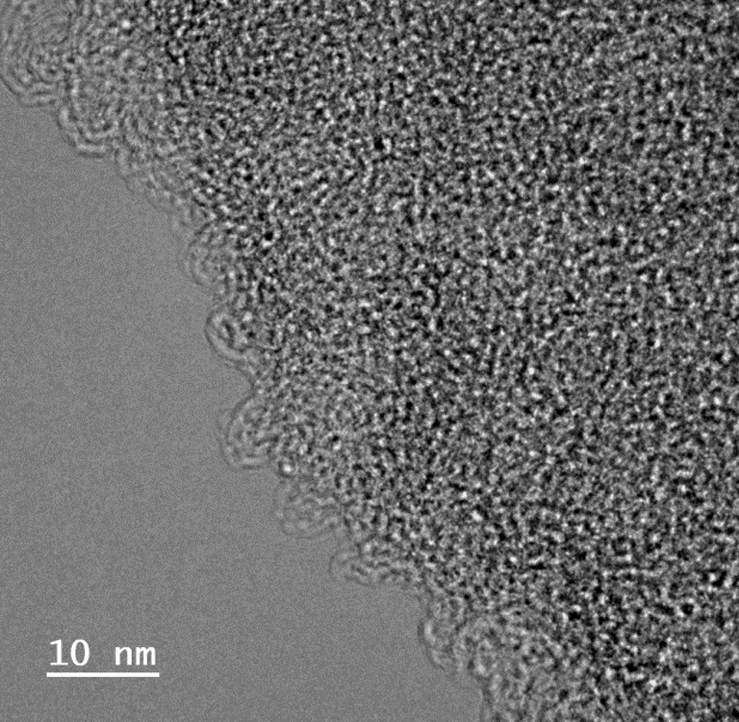
[Sudeep et al., ACS Nano 7, 7034-7040 (2013), [collaboration with Prof. Ajayan’s group]
Aswathi et al., J. Porous Mater. 21, 839 (2014)
Prathap, Shaijumon and Sureshan, Chem. Commun. 52, 1342 (2016)
Aswathi and Shaijumon, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater, 220, 21-27 (2016)